In our increasingly interconnected world, understanding the intricacies of our planet's climate system has never been more critical. Among the many components that influence global weather patterns, the jet stream plays a vital role. This fast-flowing river of air high in the atmosphere significantly affects weather systems across the globe. Recently, scientists have observed shifts in the jet stream, often linked to changes in the polar vortex.
Understanding the Jet Stream
What Is the Jet Stream?
The jet stream refers to narrow bands of strong winds that flow from west to east in the upper troposphere, typically at altitudes between 20,000 and 40,000 feet. These winds can reach speeds of over 200 miles per hour. The jet stream plays a crucial role in determining weather patterns and influencing temperature changes across the globe.
Types of Jet Streams
There are primarily two types of jet streams that characterize our atmospheric dynamics:
Polar Jet Stream: Located in the mid-latitudes, this jet stream forms at the boundary between cold polar air and warmer air from the south. It is typically stronger during winter months when the temperature gradients are more pronounced.
Subtropical Jet Stream: Positioned further south, this jet stream occurs where warm, moist air meets the cooler air of the mid-latitudes. It tends to be less variable than the polar jet stream and is generally present year-round.
The Formation of Jet Streams
Jet streams form due to a combination of the Earth's rotation and temperature differences. As the sun heats the Earth unevenly, warm air rises, creating areas of low pressure, while cold air sinks, generating high-pressure zones. The movement of air from high-pressure to low-pressure areas generates winds. The Coriolis effect, a result of the Earth's rotation, causes these winds to curve, contributing to the formation of jet streams.
The Polar Vortex
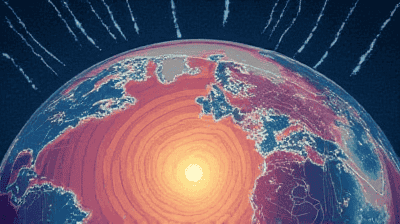
What Is the Polar Vortex?
The polar vortex refers to a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding the Earth's poles. The polar vortex exists at both the winter and summer poles but is most prominent in the winter months. When the polar vortex is stable, it remains intact and concentrated over the Arctic region. However, when it weakens or gets disrupted, it can lead to significant weather changes across the globe.
How the Polar Vortex Affects Weather
When the polar vortex is strong and stable, it effectively contains the cold Arctic air. However, disturbances in the polar vortex can cause cold air to spill southward into lower latitudes, contributing to extreme weather events such as unusually cold winters in the mid-latitudes or heatwaves as the vortex weakens.
Factors Influencing the Polar Vortex
Several factors contribute to the stability and behavior of the polar vortex, including:
Ocean Temperatures: Changes in the temperature of oceans, particularly in the North Atlantic and Pacific, can influence the polar vortex's strength.
Atmospheric Waves: Rossby waves, large-scale meandering patterns in the jet stream, can disrupt the polar vortex and shift cold air masses.
Arctic Oscillation: This climate pattern influences pressure variability in the Northern Hemisphere, affecting the polar vortex's behavior.
The Wobble of the Jet Stream
What Causes the Jet Stream to Wobble?
The jet stream is not a fixed entity; it can change in its position and intensity due to several factors, including:
Temperature Gradients: Sharp temperature differences between the polar regions and the mid-latitudes can cause the jet stream to become more pronounced and wavy, leading to more significant fluctuations in weather.
Climate Change: As global temperatures rise, the polar regions are warming faster than the equatorial regions. This unequal warming reduces the temperature gradient that typically keeps the jet stream stable, resulting in a wobbly jet stream.
Natural Variability: Natural climate patterns such as the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) can influence the jet stream's position and behavior.
Consequences of a Wobbly Jet Stream
When the jet stream becomes wobbly, it can lead to various consequences for weather patterns:
Prolonged Weather Patterns: A stagnant or wavering jet stream can result in extended periods of certain weather conditions, such as prolonged heatwaves or persistent cold spells.
Extreme Weather Events: A disrupted jet stream can contribute to increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, floods, and droughts.
Seasonal Variations: The timing of seasons can also be affected; for example, a wobbly jet stream may cause delays in the arrival of spring or fall weather.
Case Studies of Jet Stream Disruptions

The Polar Vortex Event of 2014
In the winter of 2014, a significant disruption of the polar vortex resulted in an outbreak of frigid air that swept across parts of the United States and Canada. This event brought extreme cold temperatures to regions that typically experience milder winters. The disrupted jet stream allowed cold Arctic air to plunge southward, influencing weather patterns across much of North America.
Heatwaves in Europe
In recent years, Europe has experienced intense heatwaves, attributed in part to a wobbly jet stream. This year, a significant heat dome formed as a result of atmospheric patterns, leading to record high temperatures across many countries. The jet stream's position allowed warm air to settle over the region, resulting in prolonged and extreme heat, with severe impacts on public health and agriculture.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate Change and the Polar Vortex
As climate change continues to alter global temperatures, the behavior of the polar vortex is shifting. The warming of the Arctic is leading to more frequent disruptions in the polar vortex, which, in turn, can increase the variability of the jet stream. These changes pose significant challenges to weather forecasting and understanding future climate patterns.
Feedback Loops
Changes in the jet stream and polar vortex can also create feedback loops that exacerbate climate change. For example, as Arctic ice melts, darker ocean water absorbs more heat, further warming the region and potentially altering weather patterns globally.
Impacts of Jet Stream Shifts on Ecosystems

Changes in Precipitation Patterns
Shifts in the jet stream can lead to altered precipitation patterns, with some areas experiencing excessive rainfall and flooding while others face drought. These changes in water availability directly impact ecosystems, agriculture, and freshwater resources.
Biodiversity Impacts
The changes in weather patterns associated with a wobbly jet stream can affect the distribution of plant and animal species. Some species may struggle to adapt to shifting climates, leading to declines in biodiversity and, in some cases, extinctions.
Forests and Wildfires
Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns caused by jet stream shifts can influence forest health and increase the risk of wildfires. Drier conditions combined with heatwaves make ecosystems more susceptible to fire, with cascading effects on wildlife and air quality.
Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Addressing Climate Change
Mitigating climate change is crucial for stabilizing the jet stream and polar vortex. Key strategies include:
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Transitioning to renewable energy sources and improving energy efficiency can significantly cut emissions.
Enhancing Carbon Sequestration: Protecting and restoring forests, wetlands, and other natural carbon sinks can help absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide.
Promoting Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing sustainable farming practices can reduce greenhouse gas emissions while supporting biodiversity.
Community Preparedness
Communities must be prepared to adapt to changing weather patterns. Recommendations include:
Disaster Preparedness Plans: Developing and implementing local disaster preparedness plans can help communities cope with extreme weather events.
Infrastructure Resilience: Investing in resilient infrastructure to withstand storms, floods, and other hazards is critical for safeguarding communities.
Public Awareness and Education: Educating communities about climate change and its impacts can foster a collective response to environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The relationship between the jet stream, polar vortex, and global weather is a complex and dynamic interplay. As climate change continues to influence these systems, understanding their mechanisms and impacts becomes crucial. A wobbly jet stream not only disrupts weather patterns but also poses significant challenges for ecosystems and human societies alike.
As we confront the realities of our changing climate, it is essential that we prioritize mitigation efforts, promote adaptation strategies, and work collectively to foster a sustainable future. Tackling climate change is not just about preventing extreme weather; it is about safeguarding the planet for generations to come.